优化 - 数据预处理
优化训练模式,并且处理非数字数据
Optimization
微调管道内部,超参数优化
Hyper-parameters optimization
构建管道和准备数据
构建管道
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
pipe = make_pipeline(MinMaxScaler(), SGDClassifier(max_iter=1000))
2
3
4
5
查看管道参数
print(pipe.get_params())
准备数据
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X, y = load_digits(return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, stratify=y, random_state=12)
2
3
4
5
GridSearchCV 调优
使用GridSearchCV搜索当前训练集下的最优参数
# 使用网格搜索找到当前训练集下最优参数
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
import pandas as pd
param = {'logisticregression__C': [0.1, 1.0, 10],
'logisticregression__penalty': ['l2', 'l1']}
grid = GridSearchCV(pipe, param_grid=param, cv=3, n_jobs=1, return_train_score=True)
grid.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(grid.get_params())
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- 这里要调优的参数为
C和penalty,需要在param手动中写明 - 注意这里的
grid就是一个机器学习模型,和管道pipe,分类器clf相同 - 只有当
grid已经经过训练,并且调用了score函数后,其最优函数才会确定下来,否则不认为当前训练集已经结束
查看各参数对训练的影响以及结果
df_grid = pd.DataFrame(grid.cv_results_)
print(df_grid)
2
mean_fit_time std_fit_time mean_score_time std_score_time param_logisticregression__C ... split0_train_score split1_train_score split2_train_score mean_train_score std_train_score
0 0.126961 0.001999 0.006072 0.007825 0.1 ... 0.949889 0.953229 0.949889 0.951002 0.001575
1 0.247481 0.017783 0.000620 0.000040 0.1 ... 0.891982 0.909800 0.904232 0.902004 0.007442
2 0.425019 0.011945 0.000617 0.000032 1.0 ... 0.989978 0.988864 0.984410 0.987751 0.002406
3 1.135990 0.046367 0.000678 0.000057 1.0 ... 0.982183 0.982183 0.979955 0.981440 0.001050
4 1.080702 0.094789 0.000640 0.000035 10 ... 0.998886 0.998886 0.998886 0.998886 0.000000
5 5.193207 0.190867 0.000609 0.000019 10 ... 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 0.000000
[6 rows x 18 columns]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
查看当前训练集下最优的C/penalty
print(grid.best_params_)
{'logisticregression__C': 1.0, 'logisticregression__penalty': 'l2'}
对模型grid进行精准度测试
accuracy = grid.score(X_test, y_test)
print('Accuracy score of the {} is {:.2f}'.format(grid.__class__.__name__, accuracy))
2
Accuracy score of the GridSearchCV is 0.97
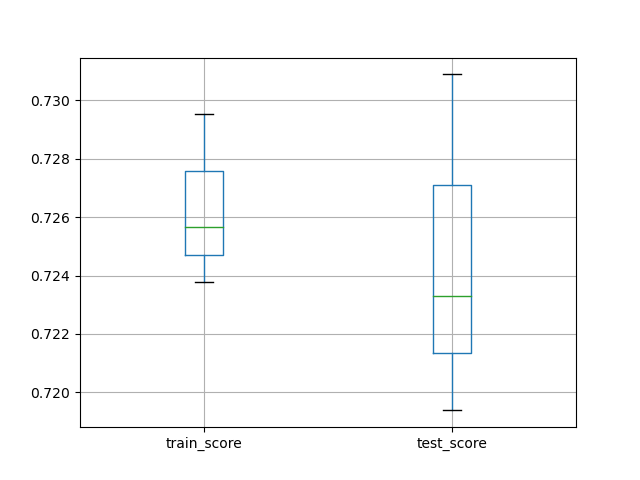
交叉验证调优后管道
前面已经提到,这里的grid是同clf/pipe一样的机器学习模型,自然可以对原数据进行交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
scores = cross_validate(grid, X, y, cv=3, n_jobs=1, return_train_score=True)
df_scores = pd.DataFrame(scores)
print(df_scores)
df_scores[['train_score', 'test_score']].boxplot()
plt.show()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
fit_time score_time test_score train_score
0 23.017125 0.000651 0.928214 0.985810
1 25.200372 0.000676 0.946578 0.997496
2 23.103306 0.000675 0.924875 0.993322
2
3
4
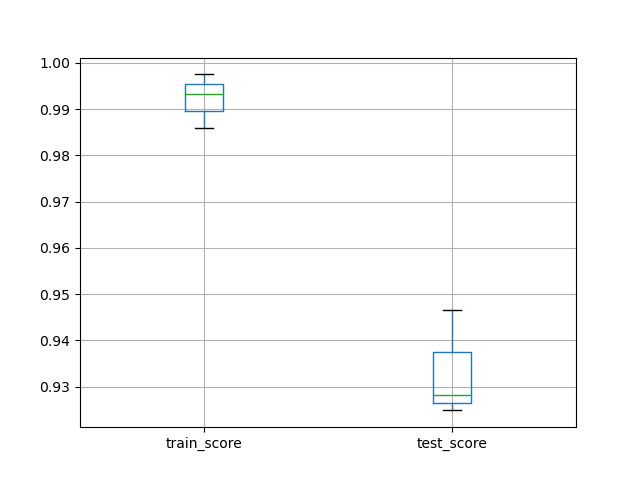
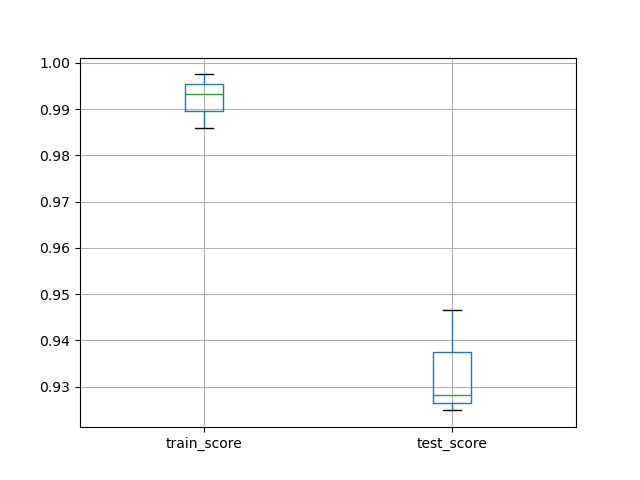
调优训练 breast_cancer
在乳腺癌数据集上对管道进行调优并训练测试
- 导入数据,分割数据
- 构建管道,调优参数
- 训练测试,交叉验证
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.metrics import balanced_accuracy_score
X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=12, stratify=y)
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
pipe = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), SGDClassifier(max_iter=1000))
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param = {'sgdclassifier__loss': ['hinge', 'log'],
'sgdclassifier__penalty': ['l2','l1']}
grid = GridSearchCV(pipe, cv=3, n_jobs=1, param_grid=param, return_train_score=True)
grid.fit(X_train, y_train)
accuracy = grid.score(X_test, y_test)
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
scores = cross_validate(grid, X, y, scoring='balanced_accuracy',
cv=3, return_train_score=True)
df_scores = pd.DataFrame(scores)
df_scores[['train_score', 'test_score']].boxplot()
plt.show()
print(grid.best_params_)
print(df_scores)
print("the accuracy is ", accuracy)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
{'sgdclassifier__loss': 'hinge', 'sgdclassifier__penalty': 'l1'}
fit_time score_time test_score train_score
0 0.031983 0.000585 0.962067 0.980303
1 0.034171 0.000492 0.949343 0.987261
2 0.032296 0.000593 0.963445 0.988076
the accuracy is 0.9440559440559441
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
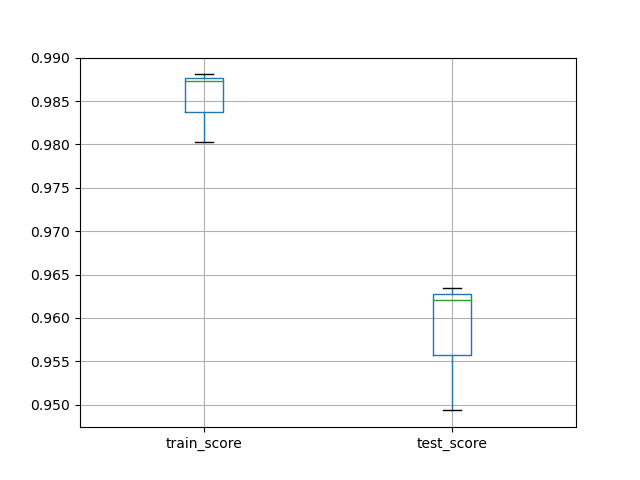
管道使用总结
使用scikit-learn十行以内训练并测试一个管道,包括数据预处理、参数调优、交叉验证
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
X, y = load_digits(return_X_y = True)
pipe = make_pipeline(MinMaxScaler(),
LogisticRegression(solver='saga', multi_class='auto', random_state=42, max_iter=5000))
param = {'logisticregression__C': [0.1, 1.0, 10],
'logisticregression__penalty': ['l2', 'l1']}
grid = GridSearchCV(pipe, param_grid=param, cv=3, n_jobs=-1)
scores = pd.DataFrame(cross_validate(grid, X, y, cv=3, n_jobs=-1, return_train_score=True))
scores[['train_score', 'test_score']].boxplot()
plt.show()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Heterogeneous Data
Heterogeneous data
处理除数字以外的数据
导入外部数据集
注意shell的位置,这里找的是当前shell路径的相对路径
- 通过
os.getcwd()获取当前路径(pwd)
import pandas as pd
import os
print(os.getcwd())
data = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data','titanic_openml.csv'), na_values='?')
print(data.head(7))
print(data.tail(4))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
先拟合再学习
从原始数据中提取出数据集
- 在该泰坦尼克模型中,自变量为年龄、性别、是否上船、恐惧等因素,因变量为是否存活
分割数据集为训练集和测试集,采用线性回归模型进行学习
y = data['survived']
X = data.drop(columns='survived')
print(y)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=12)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
clf = LogisticRegression()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
- 必然报错,因为
fit方法接收的数据集要求数据为数字型,而这里的很多数据如性别、是否上船并不是数字数据
使用管道处理非数字数据,同时使用管道标准化数字数据,这里实际上都是预处理数据的过程
- 处理非数字数据,即转化为数字数据同时处理缺失数据
SimpleImputer(strategy='constant')OneHotEncoder()
- 标准化数字数据同时处理缺失数据
SimpleImputer(strategy='mean')StandardScaler()
OneHotEncoder示例
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
ohe = make_pipeline(SimpleImputer(strategy='constant'), OneHotEncoder())
X_encoded = ohe.fit_transform(X_train[['sex', 'embarked']])
X_encoded.toarray()
2
3
4
5
[[0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
...
[0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0.]]
2
3
4
5
6
7
处理titanic数据
1、提取非数字列和数字列
col_cat = ['sex', 'embarked']
col_num = ['age', 'sibsp', 'parch', 'fare']
X_train_cat = X_train[col_cat]
X_test_cat = X_test[col_cat]
X_train_num = X_train[col_num]
X_test_num = X.test[col_num]
2
3
4
5
6
7
2、构建管道预处理数据
为什么要用管道而不是单独预处理,因为需要同时处理缺失数据
- 数字化非数字数据
- 标准化数字数据
- 处理缺失数据
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler_cat = make_pipeline(SimpleImputer(strategy='constant'), OneHotEncoder())
scaler_num = make_pipeline(SimpleImputer(strategy='mean'), StandardScaler())
X_train_cat_scaled = scaler_cat.fit_transform(X_train_cat)
X_test_cat_scaled = scaler_cat.transform(X_test_cat)
X_train_num_scaled = scaler_num.fit_transform(X_train_num)
X_tes
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
3、合并预处理后的数字数据和非数字数据,采用矩阵横向合并的方法(即合并列为一张大表)
import numpy as np
from scipy import sparse
X_train_scaled = sparse.hstack((X_train_cat_scaled,
sparse.csr_matrix(X_train_num_scaled)))
X_test_scaled = sparse.hstack((X_test_cat_scaled,
sparse.csr_matrix(X_test_num_scaled)))
2
3
4
5
6
4、现在已经有完整的数字标准化后的训练、测试数据,直接构建模型开始学习(fit)即可
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
clf = LogisticRegression()
clf.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
accuracy = clf.score(X_test_scaled, y_test)
print("Accuracy score of the {} is {:.2f}".format(clf.__class__.__name__, accuracy))
2
3
4
5
6
通过管道学习
上述过程可以概括为:
- 预处理数据
- 提取数据的非数字列和数字列
- 通过管道分别数字化、标准化处理非数字、数字数据,同时处理缺失数据
- 合并处理后的数据
- 建立模型学习并测试
和之前的学习一样,上述过程可以揉合到一个管道中进行,即构建一个含有预处理功能和学习功能的管道
这里有一个问题,就是对于数字数据和非数字数据,其预处理的方式并不同,所以管道的预处理功能应该针对特定列有不同的处理方法
这里用到sklearn.compose.make_column_transformer(transformer, col_name)合并多个管道并使之作用于不同列
- 导入数据,独立分割
data = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(), na_values='?')train_test_split
- 构建预处理管道
make_pipeline(空值处理器, 预处理器)
- 合并预处理管道
make_column_transformer((预处理管道, 列名)...)
- 构建总管道
make_pipeline(预处理器, 分类器)
- 学习并测试
fit()/score()
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import os
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data','titanic_openml.csv'), na_values='?')
y = data['survived']
X = data.drop(columns='survived')
# print(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=12)
# print(y_train)
col_cat = ['sex', 'embarked']
col_num = ['age', 'sibsp', 'parch', 'fare']
pre_cat = make_pipeline(SimpleImputer(strategy='constant'), OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown='ignore'))
pre_num = make_pipeline(SimpleImputer(strategy='mean'), StandardScaler())
from sklearn.compose import make_column_transformer
preprocessor = make_column_transformer((pre_cat, col_cat), (pre_num, col_num))
pipe = make_pipeline(preprocessor, LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs'))
pipe.fit(X_train, y_train)
accuracy = pipe.score(X_test, y_test)
print('Accuracy score of the {} is {:.2f}'.format(pipe.__class__.__name__, accuracy))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
优化管道参数
在上述包含预处理功能和学习功能的管道的基础上,在正式测试之前使用网格搜索GridSearchCV对其参数进行调优
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 调优参数
param = {'columntransformer__pipeline-2__simpleimputer__strategy': ['mean', 'median'],
'logisticregression__C': [0.1, 1.0, 10]}
grid = GridSearchCV(pipe, param_grid=param, cv=5, n_jobs=1)
grid.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(grid.score(X_test, y_test))
# 交叉验证得分
scores = cross_validate(grid, X, y, scoring='balanced_accuracy', cv=5, n_jobs=-1, return_train_score=True)
# 绘制箱型图
df_scores = pd.DataFrame(scores)
df_scores[['train_score', 'test_score']].boxplot()
plt.show()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
adult_openml.csv
使用同样的方法处理adult_openml数据集
预处理再拟合
import os
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data', 'adult_openml.csv'), na_values='?')
# print(data.head(7))
y = data['class']
X = data.drop(columns=['class', 'fnlwgt', 'capitalgain', 'capitalloss'])
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=12)
# print(y_train)
col_cat = ['workclass', 'education', 'marital-status', 'relationship', 'race', 'sex', 'native-country']
col_num = ['age', 'education-num', 'hoursperweek']
X_train_cat = X_train[col_cat]
X_test_cat = X_test[col_cat]
X_train_num = X_train[col_num]
X_test_num = X_test[col_num]
from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
cat_pipe = make_pipeline(SimpleImputer(strategy='constant'), OneHotEncoder())
num_pipe = make_pipeline(SimpleImputer(strategy='mean'), StandardScaler())
X_train_cat_scaled = cat_pipe.fit_transform(X_train_cat)
X_test_cat_scaled = cat_pipe.transform(X_test_cat)
X_train_num_scaled = num_pipe.fit_transform(X_train_num)
X_test_num_scaled = num_pipe.transform(X_test_num)
import numpy as np
from scipy import sparse
X_train_scaled = sparse.hstack((X_train_cat_scaled,
sparse.csr_matrix(X_train_num_scaled)))
X_test_scaled = sparse.hstack((X_test_cat_scaled,
sparse.csr_matrix(X_test_num_scaled)))
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
clf = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000)
clf.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
accuracy = clf.score(X_test_scaled, y_test)
print('accuracy of the {} is {:.2f}'.format(clf.__class__.__name__, accuracy))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
accuracy of the LogisticRegression is 0.83
优化管道处理
import os
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data', 'adult_openml.csv'), na_values='?')
# print(data.head(3))
y = data['class']
X = data.drop(columns=['class', 'fnlwgt', 'capitalgain', 'capitalloss'])
# print(X)
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=12)
# print(y_train)
encoder = LabelEncoder()
y_train = encoder.fit_transform(y_train)
y_test = encoder.transform(y_test)
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.compose import make_column_transformer
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
pre_cat = make_pipeline(SimpleImputer(strategy='constant'), OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown='ignore'))
pre_num = make_pipeline(SimpleImputer(strategy='mean'), StandardScaler())
col_cat = ['workclass', 'education', 'marital-status', 'relationship', 'race', 'sex', 'native-country']
col_num = ['age', 'education-num', 'hoursperweek']
preprocessor = make_column_transformer((pre_cat, col_cat), (pre_num, col_num))
# preprocessor.fit(X_train, y_train)
pipe = make_pipeline(preprocessor, LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs', max_iter=5000))
# pipe.fit(X_train, y_train)
param = {'logisticregression__C': [0.1, 1.0, 10]}
grid = GridSearchCV(pipe, param_grid=param, cv=5, n_jobs=1)
grid.fit(X_train, y_train)
accuracy = grid.score(X_test, y_test)
print('accuracy of the {} is {:.2f}'.format(grid.__class__.__name__, accuracy))
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
scores = pd.DataFrame(cross_validate(grid, X, y, scoring='balanced_accuracy', cv=3, n_jobs=-1, return_train_score=True))
print(scores)
scores[['train_score', 'test_score']].boxplot(whis=10)
plt.show()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
accuracy of the GridSearchCV is 0.83
fit_time score_time test_score train_score
0 11.303147 0.064652 0.719383 0.729532
1 12.427096 0.067366 0.730889 0.723769
2 12.042301 0.078128 0.723290 0.725647
2
3
4
5
6