深度优先搜索 - 回溯法
深度优先搜索
Deep First Search
深度优先搜索一定是递归捏
递增顺序搜索树
力扣 897:递增顺序搜索树 (opens new window)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
TreeNode* pre = new TreeNode();
TreeNode* head = new TreeNode();
public:
void inorder(TreeNode* node)
{
//当当前指针不为空
if(node == nullptr)
{
return;
}
inorder(node->left);
//令pre的右指针指向当前节点
pre->right = node;
//令当前节点的左指针为空
node->left = nullptr;
//令pre为当前指针,即下一步的前驱
pre = node;
inorder(node->right);
}
//寻找最左节点:即新生成链表的表头
void findHead(TreeNode* root)
{
TreeNode* p = root;
while(p->left != nullptr)
{
p = p->left;
}
head = p;
}
TreeNode* increasingBST(TreeNode* root)
{
findHead(root);
inorder(root);
return head;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
二叉搜索树的范围和
力扣 938:二叉搜索树的范围和 (opens new window)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
int res = 0;
public:
void inorder(TreeNode* root, int low, int high)
{
if(root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
inorder(root->left, low, high);
if(root->val >= low && root->val <= high)
{
res += root->val;
}
inorder(root->right, low, high);
}
int rangeSumBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high)
{
inorder(root, low, high);
return res;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
二叉树的中序遍历
力扣 94:二叉树的中序遍历 (opens new window)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root!=null && root.left!=null)
inorderTraversal(root.left);
if(root!=null)
list.add(root.val);
if(root!=null && root.right!=null)
inorderTraversal(root.right);
return list;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
二叉树的最近祖先
力扣 236:二叉树的最近公共祖先 (opens new window)
递归,深度优先搜索
明确 root “是 q 和 p 公共祖先” 的条件:(l&&r) || ((root==p||root==q)&&(l||r)
l:指左子树为 p 或 q 的祖先;r:指右子树为 p 或 q 的祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeNode res;
public boolean dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q){
if(root==null){
return false;
}
boolean l = dfs(root.left, p, q);
boolean r = dfs(root.right, p, q);
if((l&&r) || ((root==p||root==q)&&(l||r))){
res = root;
}
if(l || r || root==p || root==q){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
dfs(root, p, q);
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
路径总和
力扣 112:路径总和 (opens new window)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private boolean flag = false;
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum){
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val == targetSum){
flag = true;
}
int newTarget = targetSum - root.val;
dfs(root.left, newTarget);
dfs(root.right, newTarget);
}
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root, targetSum);
return flag;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
连接词
力扣 472:连接词 (opens new window)
public class Solution {
static class Trie{
public Trie[] children;
public boolean isEnd;
public Trie(){
children = new Trie[26];
isEnd = false;
}
}
//字典树
private Trie trie = new Trie();
//将单词插入字典树
public void insert(String word){
Trie p = trie;
int n = word.length();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
int index = c-'a';
if(p.children[index] == null){
p.children[index] = new Trie();
}
p = p.children[index];
}
p.isEnd = true;
}
public boolean dfs(String word, int start){
//当已经搜索到最后一位,说明该词被连接而成
if(word.length() == start){
return true;
}
Trie p = trie;
for(int i = start; i < word.length(); i++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
int index = c-'a';
if(p.children[index] == null){
return false;
}
p = p.children[index];
if(p.isEnd){
//深度优先搜索
if(dfs(word, i+1)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public List<String> findAllConcatenatedWordsInADict(String[] words){
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(words, (a, b)-> {
return a.length()-b.length();
});
for(String word: words){
if(word.length() == 0){
continue;
}
if(dfs(word, 0)){
res.add(word);
} else {
insert(word);
}
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
猫和老鼠
力扣 913:猫和老鼠 (opens new window)
在一场信息公开的游戏中,总有一方有一种方法使之不会输
package com.solution;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MouseCatGame {
private static final int catWin = 2;
private static final int draw = 0;
private static final int mouseWin = 1;
private int n;
private int[][][] dp;
private int[][] graph;
public int mouseCatGame(int[][] graph){
n = graph.length;
dp = new int[n][n][2*n];
for(int[][] i: dp){
for(int[] j: i){
Arrays.fill(j, -1);
}
}
this.graph = graph;
return getRes(1, 2, 0);
}
public int getRes(int mouse, int cat, int steps){
if(steps >= 2*n){
return draw;
}
if(dp[mouse][cat][steps] < 0){
if(mouse == 0){
dp[mouse][cat][steps] = mouseWin;
} else if(mouse == cat){
dp[mouse][cat][steps] = catWin;
} else{
getNextRes(mouse, cat, steps);
}
}
return dp[mouse][cat][steps];
}
public void getNextRes(int mouse, int cat, int steps){
int curMove = steps%2 == 0 ? mouse:cat;
int defaultRes = curMove==mouse ? catWin:mouseWin;
int res = defaultRes;
for(int nextStep: graph[curMove]){
if(curMove == cat && nextStep == 0){
continue;
}
int mouseNextStep = curMove==mouse ? nextStep:mouse;
int catNextStep = curMove==cat ? nextStep:cat;
int nextRes = getRes(mouseNextStep, catNextStep, steps+1);
if(nextRes != defaultRes){
res = nextRes;
if(res != draw){
break;
}
}
}
dp[mouse][cat][steps] = res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
最长递增子序列的个数
力扣 673:最长递增子序列的个数 (opens new window)
dp[i]记录当前位置能构成的最长递增子序列的长度对
dp[i]==maxLength的位置进行深度优先搜索,找到能构成其最长递增子序列的道路总数,返回条件为dp[j]==1 && nums[j]<pre,其中pre为上一层的数大小
class Solution {
private int[] dp;
private int res;
public int buildDp(int[] nums){
res = 0;
int n = nums.length;
dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = 1;
int maxLength = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int d = 0, j;
for(j = i-1; j >= 0; j--){
if(nums[j] < nums[i] && dp[j] > d){
d = dp[j];
}
}
dp[i] = d+1;
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, dp[i]);
}
return maxLength;
}
public void dfs(int index, int pre, int[] nums){
if(dp[index] == 1){
if(nums[index] < pre){
res++;
}
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++){
if(dp[i] == dp[index]-1 && nums[i] < nums[index]){
dfs(i, nums[index], nums);
}
}
}
public int findNumberOfLIS(int[] nums){
int n = nums.length;
int maxLength = buildDp(nums);
if(maxLength == 1){
return n;
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
if(dp[i] == maxLength){
dfs(i, maxLength, nums);
}
}
return res;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
累加数
力扣 306:累加数 (opens new window)
外两层循环枚举第一、第二结束点控制变量(
第一结束点+1==第二起始点)内一层循环枚举第三结束点(
第二结束点+1==第三起始点)若
pre+cur==next,向后搜索下一组数,直到index==n-1,即第三结束点为串末尾,返回true若
pre+cur<next,跳出本次循环,因为在第三结束点向后移动的过程中,next越来越大若
pre+cur>next,向后循环遍历第三结束点,增大next
package com.solution;
public class IsAdditiveNumber {
public boolean isAdditiveNumber(String nums){
int n = nums.length();
char[] charNums = nums.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i++){
if(charNums[0] == '0' && i > 0){ return false; }
long pre = Long.parseLong(nums.substring(0, i+1));
for(int j = i+1; j < n-1; j++){
if(charNums[i+1] == '0' && j > i+1){
continue;
}
long cur = Long.parseLong(nums.substring(i+1, j+1));
if(dfs(nums, pre, cur, n, j)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean dfs(String nums, long pre, long cur, int length, int index) {
//退出条件
if (index == length-1) {
return true;
}
for (int i = index + 1; i < length; i++) {
if (nums.charAt(index + 1) == '0' && i > index + 1) { return false; }
long next = Long.parseLong(nums.substring(index + 1, i + 1));
System.out.println(pre + "+" + cur + " " + next + " " + i);
if (next > pre + cur) { return false; }
if (next == pre + cur) { return dfs(nums, cur, next, length, i); }
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
IsAdditiveNumber ian = new IsAdditiveNumber();
System.out.println(ian.isAdditiveNumber("112358"));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
路径总和 II
力扣 113:路径总和 II (opens new window)
- 深度搜索,递归过程
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(!root){
return res;
}
vector<int> vec;
dfs(root, targetSum, vec);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* node, int targetSum, vector<int>& fact){
if(!node->left && !node->right){
if(node->val == targetSum){
fact.push_back(node->val);
res.push_back(fact);
}
fact.clear();
}
fact.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left){
vector<int> left(fact);
dfs(node->left, targetSum-node->val, left);
}
if(node->right){
vector<int> right(fact);
dfs(node->right, targetSum-node->val, right);
}
fact.clear();
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
钥匙和房间
力扣 841:钥匙和房间 (opens new window)
- 遍历房间中的钥匙,用 flags[i] 表示第 i 个房间是否被访问过
- 再次访问到直接跳过,未访问到则访问并遍历该房间中的钥匙
- 如果 flags 中存在 false,则说明未遍历完
- 因为整个图只有一个入口,即 rooms[0],如果从磁入口深度遍历不完,则说明该图无法通过 rooms[0] 到达所有节点
Solution {
public:
bool canVisitAllRooms(vector<vector<int>>& rooms) {
vector<int> flags(rooms.size(), 0);
dfs(rooms, flags, 0);
for(auto& flag: flags){
if(!flag){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<int>& flags, int index){
if(flags[index]){
return;
}
vector<int> keys = rooms[index];
flags[index] = 1;
for(auto& key: keys){
dfs(rooms, flags, key);
}
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
岛屿数量
200. 岛屿数量 - 力扣(Leetcode) (opens new window)
- 找到为 '1' 的节点,深度搜索附近为 '1' 的节点
- 被访问过的 '1' 节点需要被标记为 '2',和海洋('0')、未被访问的岛屿('1')做区分
class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
res++;
dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, int x, int y){
if(x < 0 || x >= grid.size() || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].size()){
return;
}
if(grid[x][y] != '1'){
return;
}
grid[x][y] = '2';
dfs(grid, x-1, y);
dfs(grid, x+1, y);
dfs(grid, x, y-1);
dfs(grid, x, y+1);
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
和 547. 省份数量 - 力扣(Leetcode) (opens new window) 思路差不太多,主要考虑如何标记已访问节点和遍历的边界
被围绕的区域
首先判断是否被包围,若被包围,一次性修改所有相连的 'O',否则不做修改
要注意边界上的 'O' 要求始终返回不被包围的信息,于是不被标记为已访问,以免直接跳过返回 true
class Solution {
public:
void solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> visited(m, vector<int>(n));
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(board[i][j] == 'O' && !visited[i][j]){
if(encircled(board, i, j, visited)){
cout << i << " " << j << endl;
tag(board, i, j);
}
}
}
}
}
void tag(vector<vector<char>>& board, int i, int j){
if(i < 0 || i >= board.size() || j < 0 || j >= board[0].size()-1){
return;
}
if(board[i][j] == 'X'){
return;
}
board[i][j] = 'X';
tag(board, i-1, j);
tag(board, i+1, j);
tag(board, i, j-1);
tag(board, i, j+1);
}
bool encircled(vector<vector<char>>& board, int i, int j, vector<vector<int>>& visited){
if(board[i][j] == 'X' || visited[i][j]){
return true;
}
if(i == 0 || i == board.size()-1 || j == 0 || j == board[0].size()-1){
return false;
}
visited[i][j] = true;
bool left = encircled(board, i, j-1, visited);
bool right = encircled(board, i, j+1, visited);
bool up = encircled(board, i-1, j, visited);
bool down = encircled(board, i+1, j, visited);
return left && right && up && down;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
回溯问题
在 dfs 的基础上,增加回退和剪枝的功能,本质上还是一个 dfs
所有可能的路径
797. 所有可能的路径 - 力扣(Leetcode) (opens new window)
- 给你一个有
n个节点的 有向无环图(DAG),请你找出所有从节点0到节点n-1的路径并输出
利用栈弹出使用过的节点,而非不断构造新的空间压入
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> stk;
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
stk.push_back(0);
dfs(graph, 0, graph.size()-1);
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& graph, int cur, int target){
if(cur == target){
res.push_back(stk);
return;
}
for(auto& next: graph[cur]){
stk.push_back(next);
dfs(graph, next, target);
stk.pop_back();
}
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
子集
78. 子集 - 力扣(Leetcode) (opens new window)
- 数组元素互不相同,无需剪枝
- 从上往下(树的深度)枚举所有情况
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> path;
backtrack(nums, path, 0);
return res;
}
void backtrack(vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& path, int start){
res.push_back(path);
for(int i = start; i < nums.size(); i++){
path.push_back(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums, path, i+1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
90. 子集 II - 力扣(Leetcode) (opens new window)
数组中有重复元素,需要剪枝
- 先排序,使重复元素相邻
- 再在遍历时,跳过重复元素(因为在同一层已经选中了该元素,再选,其子树均重复记录)
全排列
46. 全排列 - 力扣(Leetcode) (opens new window)
- 不断从头到尾进行遍历,暴搜
- 用数组动态标记访问过的元素
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> visited;
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
visited = vector<int>(nums.size(), 0);
vector<int> stk;
backtrack(nums, stk);
return res;
}
void backtrack(vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& stk){
int n = nums.size();
if(stk.size() == n){
res.push_back(stk);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(visited[i]){
continue;
}
stk.push_back(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
backtrack(nums, stk);
stk.pop_back();
visited[i] = false;
}
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
进阶版本:47. 全排列 II - 力扣(Leetcode) (opens new window)
需要考虑去重(剪枝)问题,关键在于
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && !visited[i-1]){
continue;
}
2
3
4
5
组合总和
39. Combination Sum - 力扣(Leetcode) (opens new window)
在数组中找到所有和为 target 的不重复的组合
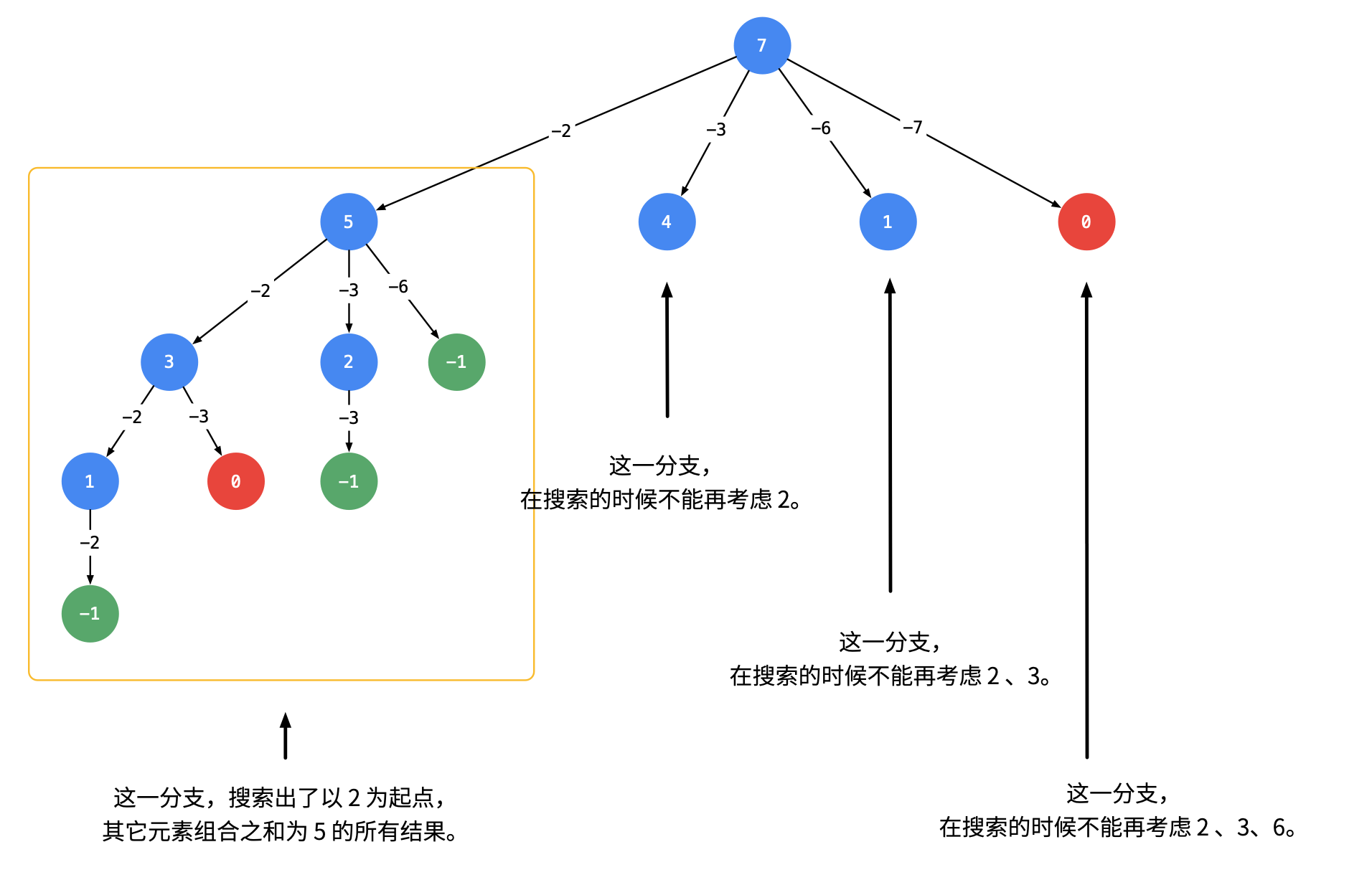
关键在于:同一层不能遍历相同的元素,如果能够遍历将出现很多重复组合,如[1,2,4], [1,4,2], [4,1,2],这个问题将退化为上一题全排列
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
int n = candidates.size();
vector<int> stk;
backtrack(candidates, target, stk, 0);
return res;
}
void backtrack(vector<int>& candidates, int target, vector<int>& stk, int start){
if(target <= 0){
if(target == 0) { res.push_back(stk); }
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.size(); i++){
int cur = candidates[i];
stk.push_back(cur);
backtrack(candidates, target-cur, stk, i);
stk.pop_back();
}
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
进阶版:40. 组合总和 II - 力扣(Leetcode) (opens new window)
- 每个数字每个组合只能出现一次,需要去重
- 同样每层不能重复选取同一元素
回溯函数
- 排序数组,相邻的相同元素,若前者未被访问,则直接跳过
- 因为是从左往右便利的,若后者当前访问,前者未访问,这一过程在上一轮肯定发生过,于是跳过
- 这一过程是指:两个相同元素占用树相同的两层
- 用
visited数组标记被访问过的元素,进入下一轮之前取消标记
void backtrack(vector<int>& candidates, int target, vector<int>& stk, int start){
if(target <= 0){
if(target == 0) { res.push_back(stk); }
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.size(); i++){
if(visited[i]){
continue;
}
if(i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i-1] && !visited[i-1]){
continue;
}
int cur = candidates[i];
stk.push_back(cur);
visited[i] = true;
backtrack(candidates, target-cur, stk, i+1);
stk.pop_back();
visited[i] = false;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20

